Flex circuit manufacturing uses two drilling methods: mechanical drilling and laser drilling. Each technique has its advantages, making it essential to select the right one based on application requirements, material properties, and cost considerations.
Mechanical Drilling for Flex Circuits
Mechanical drilling uses rotating drill bits to create holes in circuit substrates. This is a traditional method that is widely used for larger via sizes and thicker materials.
Advantages of Mechanical Drilling:
 Cost-Effective for Larger Vias: Best suited for vias above 0.15 mm (6 mils), reducing production costs.
Cost-Effective for Larger Vias: Best suited for vias above 0.15 mm (6 mils), reducing production costs. - High Throughput: Faster drilling for high-volume production of standard-sized vias.
- Well-Established Process: Proven reliability with decades of use in flex circuit manufacturing.
- Smooth Hole Walls: Reduces the risk of material damage when drilling thicker flex circuits.
Laser Drilling for Flex Circuits
Laser drilling uses high-energy beams to vaporize material, creating precise microvias without physical contact, making this method ideal for miniaturized and high-density flex circuits.
Advantages of Laser Drilling:
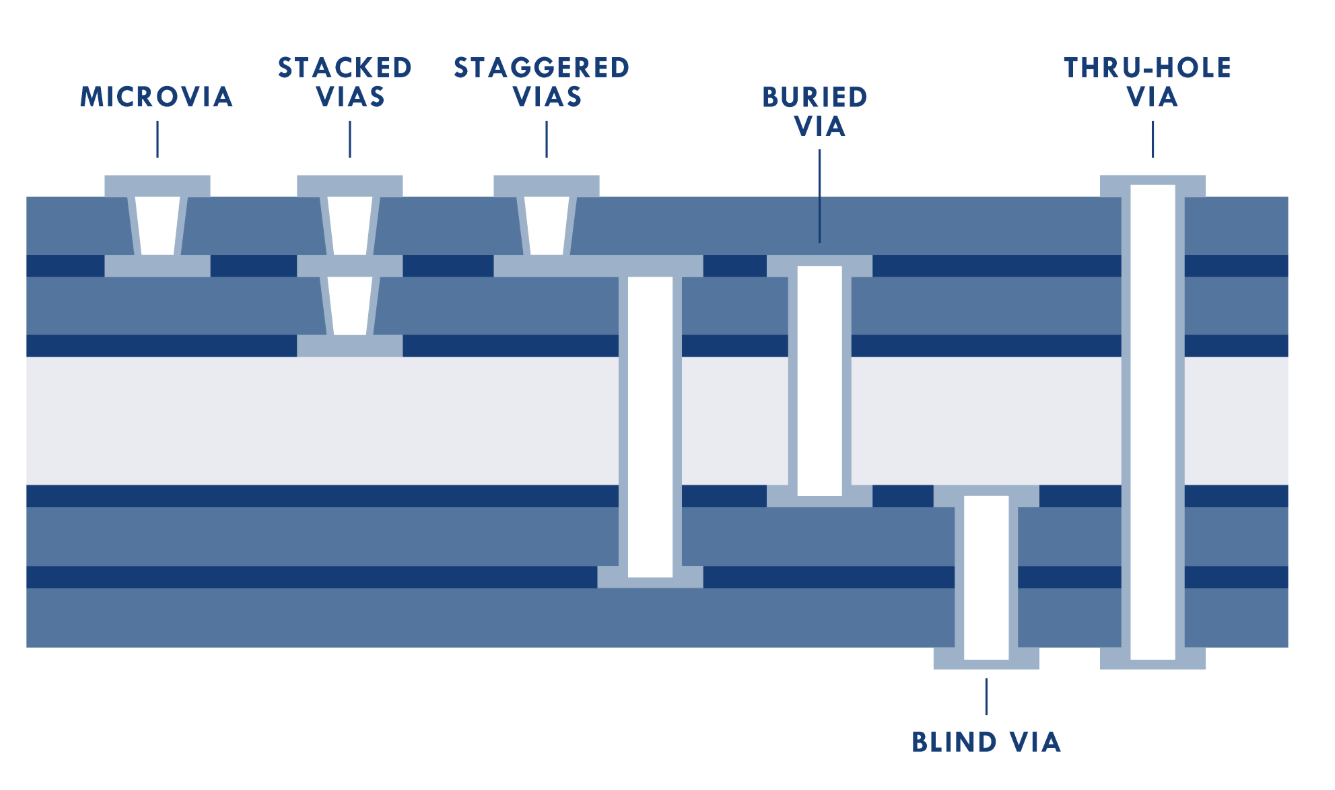
 Superior Precision: Can create microvias as small as 0.025 mm (1 mil), essential for HDI (high-density interconnect) designs.
Superior Precision: Can create microvias as small as 0.025 mm (1 mil), essential for HDI (high-density interconnect) designs. - No Mechanical Stress during the manufacturing process
- Higher Design Flexibility: Supports blind, buried, and stacked vias for compact circuit layouts.
- Effective for Thin Materials
Both mechanical and laser drilling offer distinct advantages in flex circuit manufacturing. For large-scale, cost-sensitive production, mechanical drilling is often preferred. However, for miniaturized, high-density, and high-performance applications, laser drilling is the superior choice.
Understanding your design requirements will help determine the best drilling method for your application. Need expert guidance? Contact us below to find the best drilling solution for your flex circuit needs.


 Superior Precision: Can create microvias as small as 0.025 mm (1 mil), essential for HDI (high-density interconnect) designs.
Superior Precision: Can create microvias as small as 0.025 mm (1 mil), essential for HDI (high-density interconnect) designs.